Numerical simulation
Development of a subgrid turbulent combustion model (LES)
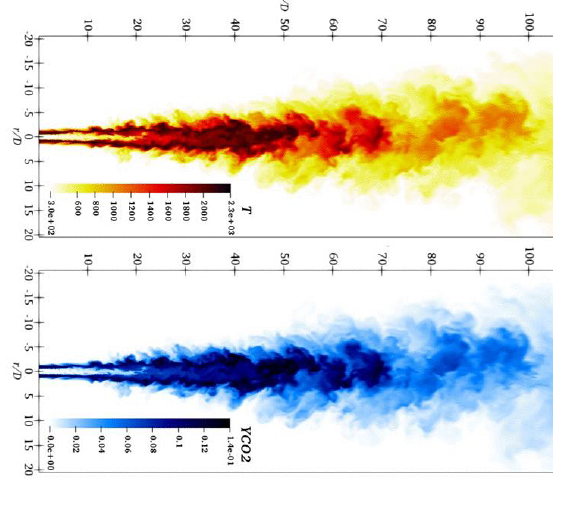
In simulating turbulent diffusion flames, it is necessary to use a mathematical model to represent the effects of concentration and temperature fluctuations caused by turbulence on chemical reactions. In this study, we are improving the assumed PDF method using a multivariable beta function for large eddy simulation (LES). We are also performing simulations using the PaSR method, which has been frequently used in simulations for MILD combustion in recent years.
Development of a turbulent combustion model for RANS simulations (RANS)

RANS (Reynolds averaged Navier-Stokes equations) simulations have a lower computational load than LES, making them a practical simulation method. However, unlike LES, which directly solves grid-scale turbulence motion and flames, The accuracy of RANS simulations highly depends on the turbulent combustion model , and hence it is essential to develop a highly accurate turbulent combustion model for RANS. In this study, we are improving the assumed PDF based on a multivariable beta function and developing a method that combines it with PaSR method.
Development of a neural network to predict mean reaction rates (ML)
In turbulent flame simulations, the computational load of reaction terms is extremely high. We aim to speed up simulations by training a neural network on combustion reactions. In this research, we aim to improve the accuracy of training by improving the pre-processing method.
Investigation of NOx production route in diffusion flames doped with water vapor (Emul)
In a combustion where excess water is added, such as in emulsion combustion, the pathway of nitrogen oxide production differs significantly from that in a conventional combustion. In this study, we perform numerical simulation of a counterflow laminar diffusion flame with added water, and investigate the effect of water addition on the elementary reactions involved in the production of nitrogen oxides.
RANS simulations of diesel combustion in a constant volume chamber (Diesel)
To date, Power Engineering Laboratory has conducted diesel combustion experiments in constant-volume combustion chambers of various shapes. In this study, we are going to perform RANS simulations of these experiments and verify the accuracy of the turbulent combustion model used in the simulations.
Contact
Power Engineering Laboratory
Energy System Dept.,
Tokushima University
Minamijosanjimacho 2-1
Tokushima 770-8506
JAPAN
TEL.081-88-6569563
FAX.081-88-6569124
