Experimental study
Click photographs to enter details
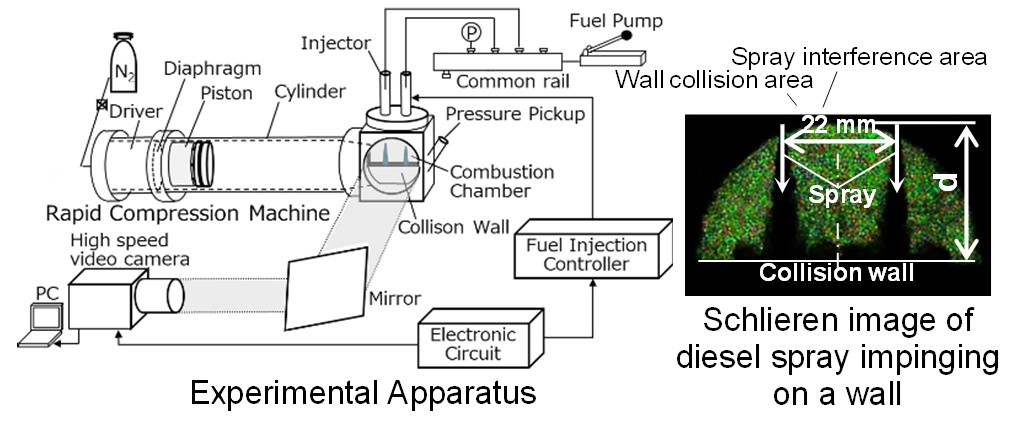
Diesel spray combustion with wall impingement and spray interaction (Spray)
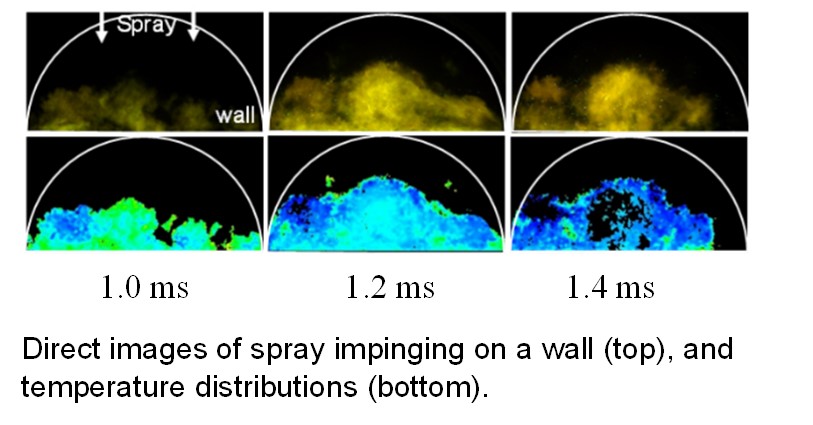
Diesel spray is injected from two injectors onto a wall maintained at a constant temperature, and ignited. We are investigating the effects of the interaction of these sprays with the wall and the interaction between the sprays.
Effects of combustion chamber shape on the diesele combustion (RCM)
Development of a spray nozzle that emulsifies without using surfactants (Emul)
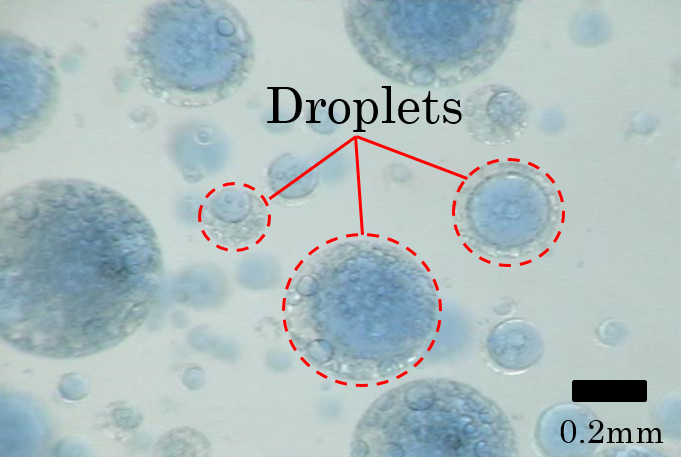
We are focusing on the water-emulsified combustion method of biomass fuel to solve problems such as increased costs and fuel stability. Rapid internally mixing injector (RIM injector) capable of rapidly mixing water as a means of emulsification of fuel just before injection is developed to improve emissions such as NOx. The picture on the right shows droplets of emulsified fuel injected from RIM injector.
High temperature air combustion (HiTAC)
High-temperature air combustion is a combustion technology that can simultaneously improve thermal efficiency through exhaust heat recovery and reduce nitrogen oxide emissions. In this study, we aim to clarify the effect of burner configuration on nitrogen oxide emissions from high-temperature air combustion (high-temperature air spray combustion) using liquid fuel, in order to establish combustion technology using vegetable oil and heavy oil as fuel.
Turbulent lifted flame (FLAME)

The liftoff height of a turbulent flame is significantly affected by the surrounding air flow velocity. In this study, we developed a model to predict the increasing liftoff height resulting from the high velocity of surrounding air flow.
Contact
Power Engineering Laboratory
Energy System Dept.,
Tokushima University
Minamijosanjimacho 2-1
Tokushima 770-8506
JAPAN
TEL.081-88-6569563
FAX.081-88-6569124
